Understanding market cycles sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
Market cycles in the financial world are a fascinating phenomenon that impacts economies globally. By delving into the intricacies of market cycles, we can uncover the underlying patterns and behaviors that drive economic trends.
Introduction to Market Cycles
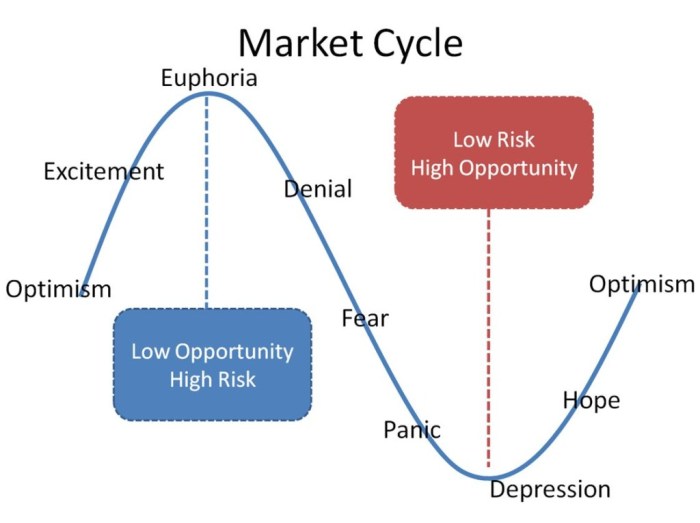
Market cycles are a fundamental concept in the financial world that describe the recurring patterns of growth and decline in financial markets. These cycles are driven by various factors such as economic conditions, investor sentiment, and market psychology.
Phases of a Typical Market Cycle
- Expansion: This phase is characterized by increasing economic activity, rising stock prices, and high investor optimism. Companies experience growth, and the overall market sentiment is positive.
- Peak: At the peak of the cycle, stock prices reach their highest levels, and investor confidence is at its peak. This is often followed by a period of stagnation or decline.
- Contraction: In this phase, economic activity slows down, stock prices start to decline, and investor confidence wanes. Companies may struggle, leading to layoffs and reduced spending.
- Trough: The trough represents the lowest point in the cycle, with stock prices at their lowest and investor sentiment extremely negative. However, this phase also sets the stage for the next expansion.
Key Indicators of Market Cycle Transitions
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates can signal shifts in market cycles. Lower interest rates often stimulate economic growth, while higher rates can lead to a slowdown.
- Unemployment Rates: Rising unemployment rates may indicate an economic contraction, while declining unemployment rates suggest an expansion phase.
- Corporate Earnings: The performance of companies in terms of earnings can provide insights into the phase of the market cycle. Strong earnings growth is typically associated with an expansion phase.
- Consumer Confidence: The confidence of consumers in the economy can impact their spending behavior, influencing the direction of the market cycle.
Understanding the Economic Factors
Economic factors play a crucial role in influencing market cycles. Various indicators and policies shape the behavior of markets, impacting investors, businesses, and consumers alike.
Impact of Inflation and Interest Rates
Inflation and interest rates are key economic factors that significantly affect different phases of the market cycle. During periods of high inflation, purchasing power decreases, leading to a rise in prices. This can have a negative impact on consumer spending and business investments, slowing down economic growth. In contrast, low inflation rates can stimulate spending and investments, driving economic expansion.
Interest rates also play a vital role in shaping market cycles. When interest rates are high, borrowing becomes more expensive, leading to reduced consumer spending and business investments. This can result in a slowdown in economic activity and potentially trigger a recession. Conversely, low-interest rates can encourage borrowing and stimulate economic growth, boosting market performance.
Role of Government Policies
Government policies have a significant impact on market cycles. Fiscal policies, such as taxation and government spending, can influence consumer behavior and business investments. For example, tax cuts can stimulate spending and economic growth, while increased government spending can create demand for goods and services, driving market performance.
Monetary policies, implemented by central banks, also play a crucial role in shaping market cycles. Central banks use tools like interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing to regulate the money supply and influence economic activity. These policies can impact inflation, interest rates, and overall market stability.
Overall, understanding how economic factors such as inflation, interest rates, and government policies influence market cycles is essential for investors and policymakers to make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the financial markets.
Behavioral Finance and Market Cycles
Investor psychology plays a significant role in driving market cycles. Emotions such as fear and greed can greatly impact market behavior during different phases, leading to fluctuations in prices and overall market trends. Understanding how these behavioral factors influence investor decisions is crucial in comprehending the dynamics of market cycles.
Role of Emotions in Market Behavior
Emotions like fear and greed are known to drive market cycles. For example, during times of uncertainty or negative news, fear can lead investors to panic sell, causing a sharp decline in prices. On the other hand, when optimism is high, greed may drive investors to buy aggressively, pushing prices to unsustainable levels. These emotional reactions create waves of buying and selling, ultimately shaping the trajectory of market cycles.
Herd Mentality and Market Cycles
Herd mentality refers to the phenomenon where individuals follow the actions of a larger group, often without questioning the rationale behind those actions. In the context of market cycles, herd mentality can lead to exaggerated price movements as investors collectively react to market trends. For instance, a sudden surge in buying due to positive news can trigger a herd mentality, causing more investors to join in and further drive up prices. Similarly, a wave of selling can be sparked by panic selling among a group of investors, leading to a downward spiral in prices.
Technical Analysis in Market Cycles
Technical analysis plays a crucial role in understanding market cycles by utilizing various tools and indicators to predict future price movements. These tools help traders and investors identify key patterns and trends within market cycles, allowing for informed decision-making.
Moving averages are commonly used in technical analysis to smooth out price data and identify trends over a specific period. By calculating the average price of an asset over a set number of periods, moving averages can help traders spot potential trend reversals or continuations within a market cycle.
Trend lines are another essential tool in technical analysis that help traders visualize the direction of price movements. By connecting the lows or highs of an asset’s price over time, trend lines can indicate the overall trend and potential support or resistance levels within a market cycle.
Other indicators, such as Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), can also assist in identifying overbought or oversold conditions, as well as potential trend shifts within market cycles.
Applying Technical Analysis to Understand Market Cycles
- Traders can use moving averages to confirm trends within market cycles. For example, a crossover of short-term and long-term moving averages could signal a potential trend reversal.
- Trend lines can be applied to identify key support and resistance levels within market cycles, helping traders determine entry and exit points for their trades.
- Indicators like RSI and MACD can provide additional confirmation of potential trend changes or reversals within market cycles, offering traders valuable insights into market dynamics.
Long-Term Investment Strategies
Investing for the long term requires a different approach compared to short-term trading. Long-term investment strategies aim to capitalize on the overall growth of the market over an extended period. These strategies are suited to different phases of the market cycle, emphasizing the importance of staying invested and allowing time to smooth out market fluctuations.
Diversification in Managing Risk
Diversification is a key strategy in managing risk across market cycles. By spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographical regions, investors can reduce the impact of negative events on their portfolios. Diversification helps to ensure that losses in one area are offset by gains in others, providing a more stable overall return.
- Diversify across asset classes: Include a mix of stocks, bonds, real estate, and other asset types to spread risk.
- Invest in different industries: Avoid overexposure to a single sector by diversifying across various industries.
- Consider global investments: Investing in international markets can provide additional diversification benefits.
“Don’t put all your eggs in one basket.”
Adjusting Investment Portfolios
It’s essential to adjust investment portfolios based on the current market cycle to optimize returns and manage risk effectively. Understanding where the market is in its cycle can help investors make informed decisions about asset allocation and investment strategies.
- During the growth phase: Focus on growth-oriented assets such as stocks to capitalize on market upswings.
- During the peak phase: Consider rebalancing the portfolio by taking profits and reallocating to more defensive assets like bonds or cash.
- During the contraction phase: Look for opportunities to buy quality assets at discounted prices for long-term growth potential.
- During the trough phase: Stay patient and avoid making impulsive decisions, as markets typically recover over time.
