With Interest rates and mortgages at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling scientific with objective tone style filled with unexpected twists and insights.
Interest rates and mortgages are essential components of the housing market, influencing affordability and decision-making. Understanding their dynamics is crucial for navigating the real estate landscape effectively.
Overview of Interest Rates and Mortgages
Interest rates play a crucial role in determining mortgage rates, affecting the overall cost of borrowing for homebuyers. Understanding this relationship is essential for individuals navigating the housing market.
Interest rates refer to the percentage charged by lenders for borrowing money. Mortgage rates, on the other hand, are the interest rates specifically applied to home loans. These rates are influenced by various factors, including economic conditions, inflation, and the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy.
Impact of Interest Rates on Mortgage Payments
Changes in interest rates directly impact mortgage payments. When interest rates rise, borrowers end up paying more in interest over the life of the loan, leading to higher monthly mortgage payments. Conversely, when interest rates fall, borrowers can potentially save on interest costs and enjoy lower monthly payments.
Effect of Interest Rates on the Housing Market
Fluctuations in interest rates can have a significant effect on the housing market. High interest rates can deter potential homebuyers, reducing demand and slowing down the market. Conversely, low interest rates tend to stimulate housing activity, encouraging more buyers to enter the market and driving up home prices.
Factors Affecting Interest Rates
Interest rates are influenced by a variety of economic factors, government policies, and the actions of central banks. Understanding these factors is crucial in analyzing the dynamics of interest rates.
Economic Factors
- Supply and demand for credit: When the demand for credit is high relative to the supply, interest rates tend to increase. Conversely, when the supply exceeds demand, interest rates may decrease.
- Inflation: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time. Lenders seek higher interest rates to compensate for the expected loss in value of the money they will be repaid in the future.
- Economic growth: Strong economic growth can lead to higher interest rates as businesses and individuals are more willing to borrow to finance investments and spending.
- Unemployment rates: High levels of unemployment are often associated with lower interest rates as central banks may implement stimulative measures to encourage borrowing and spending.
Government Policies
- Monetary policy: Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, play a crucial role in setting short-term interest rates through their monetary policy decisions. By adjusting the target federal funds rate, central banks aim to achieve their economic objectives.
- Fiscal policy: Government spending and taxation policies can also impact interest rates indirectly by influencing economic growth, inflation, and overall market conditions.
Role of Central Banks
- Setting benchmark rates: Central banks establish benchmark interest rates that serve as a reference point for other interest rates in the economy.
- Regulating money supply: Central banks control the money supply through open market operations, reserve requirements, and other tools to influence interest rates and maintain price stability.
- Managing inflation: Central banks aim to keep inflation within a target range by adjusting interest rates to balance economic growth with price stability.
Types of Mortgages
When it comes to mortgages, there are various types available to borrowers. Two common types are fixed-rate mortgages and adjustable-rate mortgages. Let’s compare and contrast these two options and explore how interest rates are determined for different types of mortgages.
Fixed-Rate Mortgages vs. Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
- Fixed-Rate Mortgages: With a fixed-rate mortgage, the interest rate remains the same throughout the life of the loan. This provides borrowers with predictability and stability in their monthly payments. However, initial interest rates for fixed-rate mortgages may be slightly higher compared to adjustable-rate mortgages.
- Adjustable-Rate Mortgages: Adjustable-rate mortgages have interest rates that can change periodically based on market conditions. These mortgages often start with lower initial interest rates, making them attractive to borrowers who plan to sell or refinance before the rates adjust. However, there is a risk of rates increasing in the future, leading to higher monthly payments.
Interest Rate Determination for Different Types of Mortgages
Interest rates for mortgages are determined by various factors, including:
- The overall economy and inflation rates
- The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy
- The type of mortgage (fixed-rate or adjustable-rate)
Pros and Cons of Different Mortgage Options Based on Interest Rates
- Fixed-Rate Mortgages:
- Pros: Predictable monthly payments, protection against rising interest rates, easier budgeting.
- Cons: Higher initial interest rates, potential for missing out on lower rates in the future.
- Adjustable-Rate Mortgages:
- Pros: Lower initial interest rates, potential for lower payments in the short term.
- Cons: Uncertainty with future rate adjustments, possibility of higher payments if rates increase.
Impact of Interest Rates on Homebuyers
Interest rates play a significant role in the homebuying process, affecting the affordability of homes and influencing the decisions of potential buyers. Fluctuations in interest rates can have both positive and negative impacts on homebuyers, making it crucial for them to understand how these changes can affect their financial situation.
Effect on Affordability of Homes
Changes in interest rates directly impact the monthly mortgage payments that homebuyers need to make. When interest rates are low, borrowing costs decrease, making homeownership more affordable. On the other hand, when interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases, potentially making homes less affordable for buyers.
Strategies for Navigating Fluctuating Interest Rates
- Locking in a Rate: Homebuyers can consider locking in a fixed interest rate when rates are low to protect themselves from potential increases in the future.
- Adjusting Budget: Buyers can adjust their budget and down payment amount to compensate for higher interest rates, ensuring they can still afford the monthly payments.
- Consulting with Experts: Seeking advice from financial advisors or mortgage professionals can help buyers navigate fluctuating interest rates and make informed decisions.
Influence on Buying Decisions
Interest rates can significantly influence the decision to buy a home or refinance a mortgage. Lower interest rates can incentivize buyers to enter the market, while higher rates may deter some buyers or lead them to explore other financing options. Homebuyers need to carefully consider interest rate trends and their own financial situation before making a decision.
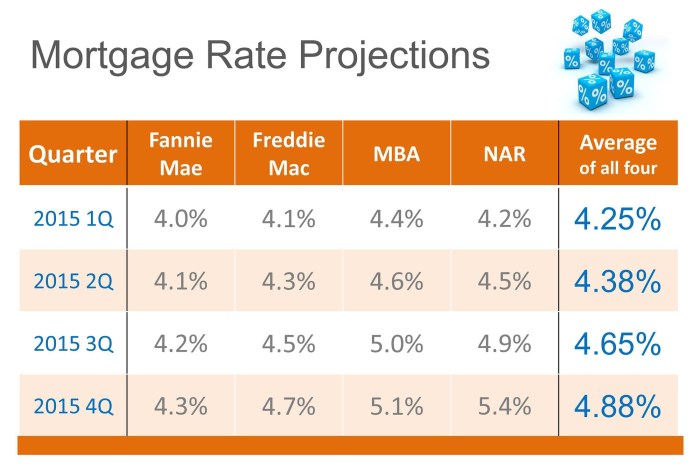
Forecasting Interest Rates
Interest rates play a crucial role in the mortgage market, influencing borrowing costs for homebuyers. Forecasting interest rates can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions regarding mortgages and other financial activities. Various methods are utilized to predict future trends in interest rates, taking into account economic indicators and market conditions.
Methods of Forecasting
- Interest Rate Models: Economists and financial analysts develop models based on historical data and economic variables to forecast interest rate movements. These models may include factors such as inflation rates, GDP growth, and central bank policies.
- Yield Curve Analysis: By examining the yield curve, which plots interest rates of bonds with different maturities, analysts can gain insights into market expectations regarding future interest rate changes. An inverted yield curve, for example, may indicate an impending economic downturn.
- Survey-based Forecasts: Surveys of economists, financial institutions, and market participants provide consensus views on future interest rate movements. These surveys can offer valuable insights into market sentiment and expectations.
Implications on Mortgage Rates
- Interest rate forecasts directly impact mortgage rates, as lenders adjust their rates based on anticipated changes in borrowing costs. Homebuyers can use interest rate forecasts to time their mortgage applications and lock in favorable rates.
- Long-term interest rate forecasts can influence the choice between fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages. Borrowers may opt for fixed-rate mortgages if interest rates are expected to rise, providing stability in monthly payments.
Role of Economic Indicators
- Key economic indicators, such as inflation rates, unemployment figures, and GDP growth, can provide valuable insights into the direction of interest rates. For example, high inflation rates may prompt central banks to raise interest rates to curb inflationary pressures.
- Market participants closely monitor economic indicators to anticipate changes in monetary policy and interest rates. By analyzing these indicators, economists and investors can form educated forecasts on future interest rate movements.
