As how to budget takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. By understanding the importance of budgeting and setting clear financial goals, individuals can pave the way towards financial stability and success. This guide will delve into the intricacies of creating, tracking, and adjusting a budget, as well as the crucial role of saving and investing.
Importance of Budgeting
Budgeting plays a crucial role in ensuring financial stability and security. By creating and following a budget, individuals can effectively manage their finances, track their expenses, and plan for the future. Let’s explore the key reasons why budgeting is essential:
Financial Stability
Creating a budget helps individuals maintain financial stability by providing a clear overview of their income and expenses. By knowing exactly how much money is coming in and going out, individuals can avoid overspending and ensure they have enough savings for emergencies.
Benefits of Creating and Sticking to a Budget
– Helps in prioritizing expenses and identifying unnecessary spending.
– Enables individuals to save for specific goals, such as buying a house or starting a business.
– Reduces financial stress and anxiety by providing a sense of control over one’s finances.
– Allows for better decision-making when it comes to financial matters.
Achieving Financial Goals
Budgeting is a powerful tool for achieving financial goals. By setting realistic targets and tracking progress through a budget, individuals can stay motivated and focused on reaching their objectives. Whether it’s saving for retirement, paying off debt, or investing in education, a well-planned budget can pave the way to financial success.
Setting Financial Goals
Setting clear financial goals is a crucial step before creating a budget. Financial goals provide a clear direction and purpose for your budgeting efforts, helping you stay motivated and focused on achieving your desired outcomes.
Short-term and Long-term Financial Goals
- Short-term Financial Goals: These are goals that you aim to achieve within a relatively short period, usually within a year. Examples include building an emergency fund, paying off credit card debt, or saving for a vacation.
- Long-term Financial Goals: Long-term goals typically span several years or even decades. Examples include saving for retirement, buying a home, or funding a child’s education.
Aligning Budgeting Strategies with Financial Objectives
Before creating a budget, it’s essential to align your budgeting strategies with your financial objectives. Here are some ways to do this:
- Evaluate Your Goals: Review your short-term and long-term financial goals to understand what you want to achieve.
- Prioritize Goals: Determine which goals are most important to you and allocate resources accordingly in your budget.
- Create a Realistic Budget: Develop a budget that reflects your financial goals, ensuring that your income and expenses are aligned with your objectives.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly track your budget and financial goals to stay on course and make adjustments as needed.
Creating a Budget
Creating a budget is essential for managing your finances effectively. It helps you track your income, expenses, and savings, ensuring that you stay on top of your financial goals. Here are the steps to create a basic budget:
Steps to Create a Basic Budget
- List Your Income: Start by listing all your sources of income, including salaries, bonuses, or any other earnings.
- Calculate Your Expenses: Track your expenses by categorizing them into fixed (rent, utilities) and variable (groceries, entertainment).
- Determine Your Savings Goals: Decide on how much you want to save each month for emergencies, retirement, or other financial goals.
- Create a Budget Template: Use a spreadsheet or budgeting app to allocate your income towards expenses, savings, and debt payments.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly review your budget to see if you are sticking to your plan. Make adjustments as needed to stay on track.
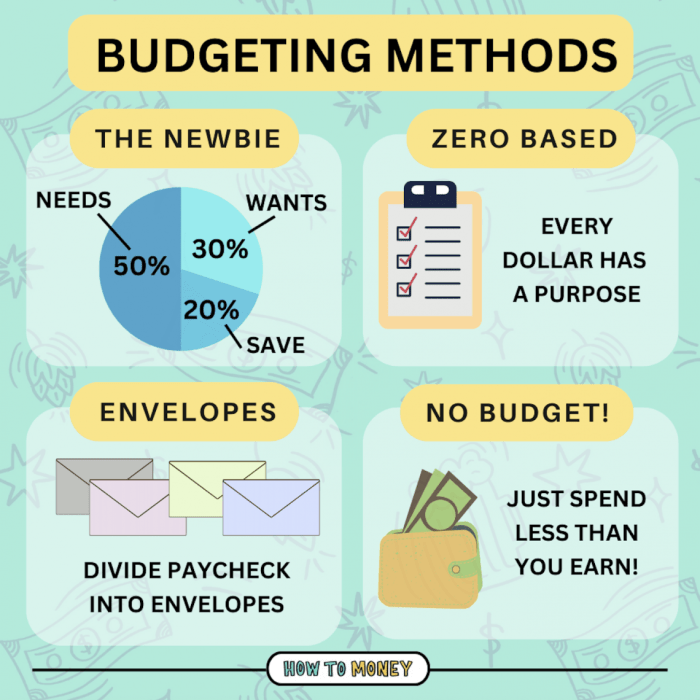
Different Budgeting Methods
- Zero-Based Budgeting: In this method, every dollar of income is assigned to an expense, savings, or debt repayment, leaving zero money unallocated.
- 50/30/20 Rule: This rule suggests allocating 50% of your income to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings and debt repayment.
Categorizing Expenses and Allocating Funds
- Category Allocation: Divide your expenses into categories like housing, transportation, groceries, entertainment, and allocate a specific amount to each category.
- Prioritize Expenses: Ensure to prioritize essential expenses like rent and utilities before allocating funds to discretionary spending.
- Emergency Fund: Allocate a portion of your income towards building an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses.
Tracking Expenses
Tracking expenses is a crucial aspect of budgeting that allows individuals to monitor their spending habits and ensure they stay within their financial limits. By keeping a close eye on expenses, individuals can make informed decisions about where to cut back and where to allocate more funds. This helps in achieving financial goals and maintaining a healthy financial status.
Importance of Regularly Reviewing Expenses
Regularly reviewing expenses is essential to identify any unnecessary spending patterns and make adjustments to stay on track with the budget. It provides insight into where the money is going and highlights areas where savings can be made. By analyzing expenses regularly, individuals can avoid overspending and work towards achieving their financial objectives effectively.
- Set aside time each week to go through your expenses, categorize them, and compare them against your budget.
- Use budgeting apps or spreadsheets to track expenses automatically and generate reports for easy analysis.
- Identify trends in your spending behavior and make necessary changes to align with your financial goals.
- Reviewing expenses regularly helps in identifying any discrepancies or errors in financial transactions that need to be addressed promptly.
Tools and Apps for Efficient Expense Tracking
There are various tools and apps available that can simplify the process of tracking expenses and provide valuable insights into spending habits. These tools offer features such as categorizing expenses, setting budget limits, and generating reports for better financial management.
- Mint: A popular budgeting app that syncs with your bank accounts and credit cards to track expenses and create budgets.
- You Need A Budget (YNAB): Focuses on giving every dollar a job, helping users track expenses and prioritize spending based on their financial goals.
- PocketGuard: Analyzes spending patterns, tracks bills, and helps users optimize their budgets for better financial outcomes.
- Personal Capital: Offers a comprehensive view of your financial life, including expenses, investments, and net worth, to aid in making informed financial decisions.
Adjusting the Budget
Adjusting the budget is a crucial step in the financial planning process. It allows individuals to adapt to changing circumstances and ensure their financial goals are still achievable.
When to Make Adjustments
- Review your budget regularly, ideally on a monthly basis, to identify any discrepancies or changes in income and expenses.
- Adjust your budget whenever there are significant changes in your financial situation, such as a pay raise, job loss, or unexpected expenses.
How to Make Adjustments
- Identify areas where you can cut back or reallocate funds to cover unexpected expenses or achieve new financial goals.
- Consider renegotiating bills or subscriptions, reducing discretionary spending, or finding additional sources of income.
Dealing with Unexpected Expenses
Unexpected expenses can throw off your budget, but there are strategies to handle them:
- Build an emergency fund to cover unforeseen costs without derailing your financial plan.
- Prioritize essential expenses and postpone non-urgent purchases until you can readjust your budget.
Reallocating Funds Within a Budget
When necessary, reallocating funds within a budget can help you stay on track with your financial goals:
- Shift funds from less critical categories to cover more pressing needs without overspending.
- Track your spending regularly to identify areas where you can redistribute funds to align with your priorities.
Saving and Investing
Saving and investing play crucial roles in a budget as they help individuals secure their financial future and achieve their long-term financial goals. Saving allows individuals to set aside money for emergencies or future expenses, while investing helps grow wealth over time through various investment vehicles such as stocks, bonds, and real estate.
Incorporating Savings and Investment Goals into a Budget
When creating a budget, it is important to allocate a portion of your income towards savings and investments. This can be done by setting specific savings goals, such as building an emergency fund, saving for a down payment on a house, or investing for retirement.
One effective way to incorporate savings and investment goals into a budget is to automate savings and investment contributions. Setting up automatic transfers from your checking account to a savings account or investment account ensures that you consistently save and invest without needing to actively remember to do so.
Building an Emergency Fund and Investing for the Future
Building an emergency fund is a critical component of financial planning. An emergency fund acts as a safety net in case of unexpected expenses or a loss of income. Financial experts recommend saving at least three to six months’ worth of living expenses in an easily accessible account, such as a high-yield savings account.
When it comes to investing for the future, it is important to diversify your investment portfolio to mitigate risks. Consider investing in a mix of stocks, bonds, and other asset classes based on your risk tolerance and investment horizon. Regularly review and rebalance your investment portfolio to ensure it aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
