Delving into Financial implications of a home purchase, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative that explores the various financial aspects associated with buying a home. From budgeting considerations to financing options, this discussion will shed light on the critical factors to consider when embarking on the journey of homeownership.
As we delve deeper into the realm of financial implications of a home purchase, it becomes evident that a thorough understanding of the costs involved is essential for making informed decisions. Let’s explore this complex yet crucial topic in detail.
Overview of Home Purchase
When it comes to purchasing a home, there are several key steps involved that buyers need to consider. Understanding the financial implications of buying a property is crucial before making such a significant investment.
Process of Purchasing a Home
- Researching the Market: Prospective buyers should start by researching the real estate market to understand current trends and pricing.
- Getting Pre-Approved for a Mortgage: Before starting the house-hunting process, it’s essential to get pre-approved for a mortgage to know your budget.
- Working with a Real Estate Agent: Engaging the services of a real estate agent can help buyers navigate the complex process of purchasing a home.
- House Hunting and Making an Offer: Once you find a property that meets your criteria, you can make an offer through your agent.
- Home Inspection and Appraisal: After the offer is accepted, a home inspection and appraisal are done to assess the condition and value of the property.
- Closing the Deal: The final step involves signing all necessary paperwork, transferring funds, and officially taking ownership of the property.
Importance of Understanding Financial Implications
- Financial Stability: Knowing the financial implications of buying a home ensures that buyers are financially stable enough to afford the purchase.
- Budgeting: Understanding the costs involved in buying a home helps buyers create a realistic budget and avoid overspending.
- Long-Term Commitment: Purchasing a home is a long-term commitment, and understanding the financial implications ensures that buyers can sustain homeownership in the future.
Budgeting for a Home Purchase
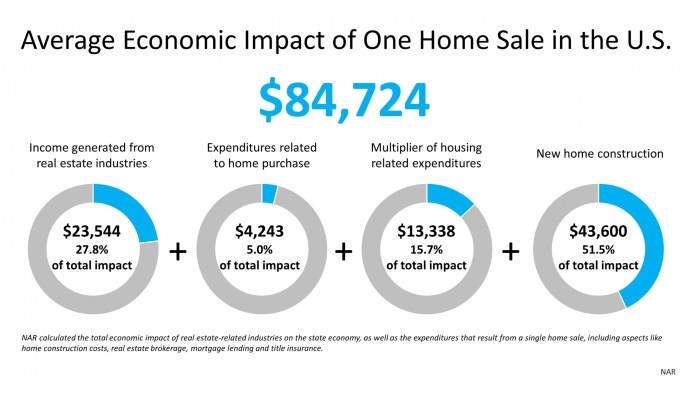
When it comes to buying a home, setting a budget is crucial to ensure you make a sound financial decision. A well-thought-out budget can help you determine how much you can afford to spend on a property without straining your finances. Here are some tips on setting a budget for buying a home:
Factors to Consider when Budgeting for a Property Purchase
- Income and Expenses: Evaluate your current income and expenses to determine how much you can allocate towards mortgage payments.
- Down Payment: Consider how much you can afford to put down as a down payment, as this will affect your monthly mortgage payments and overall loan amount.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio: Lenders typically look at your debt-to-income ratio to assess your ability to repay a mortgage. Aim for a ratio below 43% for better loan approval chances.
- Emergency Fund: Ensure you have enough savings set aside for unexpected expenses or emergencies after purchasing a home.
Significance of Creating a Realistic Budget for a Home Purchase
Creating a realistic budget for a home purchase is essential to avoid overextending yourself financially. By setting a budget, you can:
- Avoid getting into debt: A realistic budget helps prevent taking on more mortgage debt than you can comfortably repay.
- Stay within your means: Setting a budget ensures you purchase a property that aligns with your financial capabilities and long-term goals.
- Plan for future expenses: By budgeting appropriately, you can plan for ongoing homeownership costs such as maintenance, insurance, and property taxes.
Costs Involved in Buying a Home
When purchasing a home, there are various costs that buyers need to consider beyond the listing price of the property. These costs can include one-time expenses as well as ongoing financial obligations that come with homeownership. It is crucial for buyers to be aware of these costs to make informed decisions and avoid any financial surprises in the future.
One-Time Costs
- Down Payment: This is a lump sum payment made upfront towards the purchase price of the property. The amount of the down payment can vary depending on the type of mortgage and the buyer’s financial situation.
- Closing Costs: These costs include fees for services such as home inspection, appraisal, title search, and legal fees. Closing costs typically range from 2% to 5% of the purchase price.
- Moving Expenses: Buyers need to budget for the costs associated with moving their belongings to the new property, including hiring movers or renting a moving truck.
Ongoing Costs
- Mortgage Payments: This is the regular payment made towards the mortgage loan, which includes principal and interest. It is important for buyers to budget for this recurring expense.
- Property Taxes: Homeowners are responsible for paying property taxes, which can vary based on the location and value of the property. These taxes are usually paid annually or semi-annually.
- Homeowners Insurance: Insurance is essential to protect the property against damage or loss. The cost of homeowners insurance can vary depending on factors such as the property’s location, age, and construction.
Hidden Expenses
- Home Maintenance: Buyers should budget for ongoing maintenance and repairs for the property, such as HVAC servicing, roof repairs, and landscaping.
- Homeowners Association (HOA) Fees: If the property is part of a homeowners association, buyers will need to pay regular dues for maintenance of common areas and amenities.
- Utilities: Buyers should factor in the cost of utilities such as electricity, water, gas, and internet when budgeting for homeownership.
Financing Options for Home Purchase
When it comes to buying a home, there are various financing options available to potential buyers. These options can have a significant impact on the overall cost of purchasing a home and the financial implications in the long run.
Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rate Mortgages
One of the key decisions when securing financing for a home purchase is choosing between a fixed or variable interest rate mortgage. A fixed-rate mortgage offers the stability of a constant interest rate throughout the term of the loan, providing predictability in monthly payments. On the other hand, a variable interest rate mortgage fluctuates with market conditions, potentially resulting in lower initial rates but also higher risk of payment increases in the future.
Credit Score and Securing a Home Loan
Your credit score plays a crucial role in determining your eligibility for a home loan and the interest rate you’ll receive. A higher credit score typically translates to lower interest rates and more favorable loan terms, while a lower credit score may result in higher interest rates or difficulty in securing a loan. It’s essential to maintain a good credit score by making timely payments, managing debt responsibly, and monitoring your credit report regularly to improve your chances of securing a home loan at a favorable rate.
Investment Potential of Home Purchase
When considering the investment potential of buying a home, it is important to analyze various factors that can impact the return on investment, property value appreciation or depreciation, and strategies for maximizing the investment potential.
Potential Return on Investment
One of the key aspects of buying a home is the potential return on investment. This can be influenced by factors such as the location of the property, market trends, and the overall condition of the real estate market.
Factors Affecting Property Value
Several factors can affect the appreciation or depreciation of property value. These include the neighborhood, nearby amenities, economic conditions, and any renovations or improvements made to the property.
Strategies for Maximizing Investment Potential
- Regular maintenance and upgrades: By keeping the property well-maintained and making strategic upgrades, you can increase its value over time.
- Location, location, location: Choosing a property in a desirable location with good growth potential can enhance its investment value.
- Rental income: If applicable, renting out the property can provide a steady income stream and increase overall return on investment.
- Real estate market research: Staying informed about market trends and conditions can help you make informed decisions about when to buy, sell, or make improvements to your property.
