Delving into the realm of financial asset classes unveils a complex yet fascinating landscape of investment opportunities. From equities to commodities, each class offers unique characteristics and benefits worth exploring. Join us on a journey through the diverse world of financial assets.
Overview of Financial Asset Classes
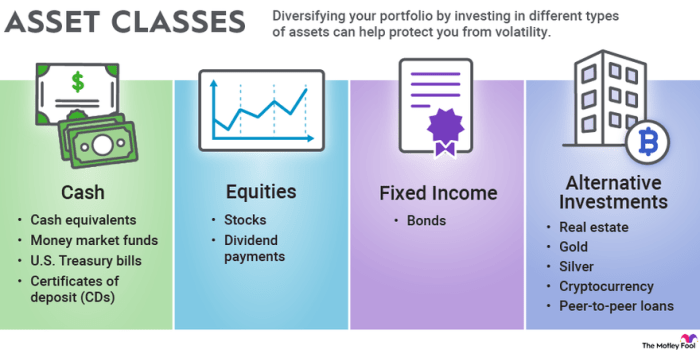
Financial asset classes are categories of investments that have similar characteristics and behaviors. They are crucial components of investment portfolios as they offer investors a range of options to diversify and manage risk effectively. By allocating investments across different asset classes, investors can achieve a balance between risk and return, ultimately optimizing their portfolios.
Types of Financial Asset Classes
- Equities: Equities represent ownership in a company and are also known as stocks. They offer potential for high returns but come with higher volatility.
- Fixed Income: Fixed income securities include bonds and other debt instruments. They provide regular interest payments and are considered less risky than equities.
- Real Estate: Real estate investments involve owning physical properties such as residential, commercial, or industrial real estate. They can provide income through rent and potential appreciation in value.
- Commodities: Commodities include raw materials like gold, oil, and agricultural products. They can act as a hedge against inflation and offer diversification benefits.
- Cash Equivalents: Cash equivalents are highly liquid and low-risk investments like Treasury bills and money market funds. They provide stability and liquidity to a portfolio.
Role of Diversification in Risk Management
Diversification across various asset classes is essential in risk management as it helps reduce the impact of market volatility on a portfolio. By spreading investments across different asset classes, investors can lower the overall risk exposure and potentially enhance returns. Diversification ensures that a downturn in one asset class does not have a significant negative impact on the entire portfolio, leading to a more stable and balanced investment strategy.
Equities as a Financial Asset Class
Equities, also known as stocks, represent ownership shares in a company. Investors who purchase equities become partial owners of the company and have the potential to benefit from the company’s profits and growth. One of the main attractions of equities is their potential for capital appreciation, as the value of the shares can increase over time.
Types of Equities
- Common Stock: Common stock represents basic ownership in a company and gives investors voting rights in corporate decisions. These stocks offer the potential for capital appreciation through price appreciation and dividends, but they also carry higher risk compared to other types of equities.
- Preferred Stock: Preferred stock is a type of equity that typically does not come with voting rights but offers priority in receiving dividends over common stockholders. Preferred stockholders also have a higher claim on company assets in the event of liquidation, providing a more stable income stream compared to common stock.
Risk-Return Profiles of Equities
Equities, especially individual stocks, are known for their higher risk-return profiles compared to other asset classes. Investing in individual stocks can be risky due to the potential for company-specific events to impact the stock price. On the other hand, diversified equity funds, such as mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs), spread the risk across a portfolio of stocks, reducing the impact of any single stock’s performance on the overall investment. Diversified equity funds typically offer a more balanced risk-return profile compared to investing in individual stocks.
Fixed Income as a Financial Asset Class
Fixed income securities are investment products that provide investors with regular income in the form of interest payments. These securities are considered to be more conservative than equities and are often used by investors seeking a steady income stream while preserving their capital. Fixed income securities play a crucial role in diversifying an investment portfolio and managing risk.
Types of Fixed Income Instruments
- Bonds: Bonds are debt securities issued by governments, corporations, or municipalities to raise capital. Investors who purchase bonds are essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for periodic interest payments and the return of the principal amount at maturity.
- Treasury Securities: Treasury securities are issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury to finance the government’s operations and pay off existing debt. These securities are considered to be among the safest investments as they are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government.
- Corporate Bonds: Corporate bonds are debt securities issued by corporations to raise funds for various purposes such as expansion, acquisitions, or debt refinancing. The interest rates on corporate bonds are typically higher than those on treasury securities to compensate investors for the higher risk associated with corporate debt.
- Municipal Bonds: Municipal bonds are debt securities issued by state and local governments to fund public projects such as infrastructure development, schools, and hospitals. Interest income from municipal bonds is often exempt from federal income tax, making them attractive to investors in high tax brackets.
Relationship between Interest Rates, Bond Prices, and Bond Yields
When interest rates rise, bond prices typically fall, and vice versa. This inverse relationship is due to the fact that existing bonds with fixed interest rates become less attractive in a rising rate environment. As a result, their prices decrease to provide a yield that is in line with the current market rates. On the other hand, when interest rates fall, bond prices tend to rise as investors are willing to pay a premium for higher yielding bonds in a low-rate environment. Bond yields move inversely to bond prices, meaning that as bond prices rise, yields decrease, and as bond prices fall, yields increase.
Real Estate as a Financial Asset Class
Real estate is considered an alternative investment class that offers the potential for both capital appreciation and rental income. Investors often turn to real estate to diversify their portfolios and hedge against market volatility.
Ways to Invest in Real Estate
Investors have various options to invest in real estate, including:
- Direct Ownership: Purchasing physical properties such as residential homes, commercial buildings, or land.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): Investing in publicly traded companies that own and manage income-producing real estate.
- Real Estate Crowdfunding Platforms: Participating in real estate projects by pooling funds with other investors through online platforms.
Factors Influencing Real Estate Investments
The performance of real estate investments can be influenced by several key factors, including:
- Location: The desirability and growth potential of the property’s location can significantly impact its value and rental income.
- Property Type: Different types of properties, such as residential, commercial, industrial, or hospitality, have varying risk and return profiles.
- Market Conditions: Economic factors, interest rates, supply and demand dynamics, and regulatory changes can all affect the real estate market’s performance.
Commodities as a Financial Asset Class
Commodities are raw materials or primary agricultural products that are traded on commodity exchanges. They can include energy sources like oil and natural gas, metals such as gold and silver, as well as agricultural products like corn and wheat.
Commodities play a crucial role in portfolio diversification by offering a unique investment opportunity that is not closely correlated with traditional assets like stocks and bonds. They can provide a hedge against inflation and geopolitical risks, as their value tends to move independently from other asset classes.
Categories of Commodities
- Energy: This category includes commodities like oil, natural gas, and electricity. Energy commodities are essential for various industries and are influenced by factors such as supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and weather conditions.
- Metals: Precious metals like gold and silver are often considered safe-haven assets during times of economic uncertainty. Industrial metals such as copper and aluminum are influenced by global economic growth and infrastructure development.
- Agricultural Products: Commodities like corn, wheat, soybeans, and coffee fall under this category. Agricultural commodities are influenced by factors such as weather conditions, crop yields, and global demand.
Cash Equivalents as a Financial Asset Class
Cash equivalents are low-risk, highly liquid assets that can be quickly converted into cash. These assets play a crucial role in providing stability and liquidity to investment portfolios.
Types of Cash Equivalents
- Money Market Funds: These are mutual funds that invest in short-term, high-quality securities such as Treasury bills and commercial paper.
- Treasury Bills: Short-term debt securities issued by the U.S. government with maturities ranging from a few days to one year.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): Time deposits offered by banks and credit unions with fixed interest rates and maturity dates.
