Beginning with Building a financial portfolio, the narrative unfolds in a compelling and distinctive manner, drawing readers into a story that promises to be both engaging and uniquely memorable.
Delving into the realm of financial portfolios opens up a world of possibilities for investors looking to secure their financial future through strategic asset allocation and risk management.
Importance of Diversification in Financial Portfolio
Diversification is a key strategy in building a financial portfolio that involves spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographical regions to reduce risk and improve overall returns.
Benefits of Diversification
- Diversification helps mitigate risks by reducing the impact of a single investment’s poor performance on the overall portfolio.
- It can enhance long-term returns by capturing the growth potential of various sectors and regions, balancing out losses in one area with gains in another.
- By diversifying, investors can lower the volatility of their portfolio, making it more stable and less susceptible to market fluctuations.
- It provides a hedge against unforeseen events or economic downturns, as different assets may react differently to changing market conditions.
Consequences of Not Diversifying
- Failure to diversify can expose the portfolio to higher levels of risk, as a concentrated position in a single asset or sector can lead to significant losses if that area underperforms.
- Without diversification, the portfolio is more vulnerable to market volatility, as any adverse events impacting a specific asset class could have a magnified effect on the overall investment.
- Lack of diversification can limit potential returns, as the portfolio’s growth is tied solely to the performance of a few investments, rather than benefiting from broader market movements.
Types of Assets for Inclusion in a Financial Portfolio
Investors have a variety of assets to choose from when building their financial portfolios. Each type of asset comes with its own set of characteristics and risks that need to be carefully considered in order to achieve a well-balanced and diversified portfolio.
Stocks
Stocks represent ownership in a company and are considered one of the higher-risk assets in a portfolio. They offer the potential for high returns but also come with the risk of price volatility and potential losses. It is important to research and analyze individual companies before investing in their stocks to mitigate risks.
Bonds
Bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations. They are generally considered lower-risk assets compared to stocks, as they provide a fixed income stream and return of principal at maturity. However, bond prices can be affected by interest rate changes and credit risk, so it’s crucial to diversify across different types of bonds.
Real Estate
Real estate investments involve buying property with the expectation of generating rental income or capital appreciation. Real estate can provide a hedge against inflation and diversification from traditional financial assets. However, it also comes with risks such as market fluctuations, maintenance costs, and liquidity issues.
Balancing High-risk and Low-risk Assets
Balancing high-risk and low-risk assets in a portfolio is essential to manage overall risk and optimize returns. High-risk assets like stocks can provide growth potential, while low-risk assets like bonds can offer stability and income. Finding the right mix of assets based on individual risk tolerance and investment goals is key to building a resilient portfolio.
Strategies for Building a Strong Financial Portfolio
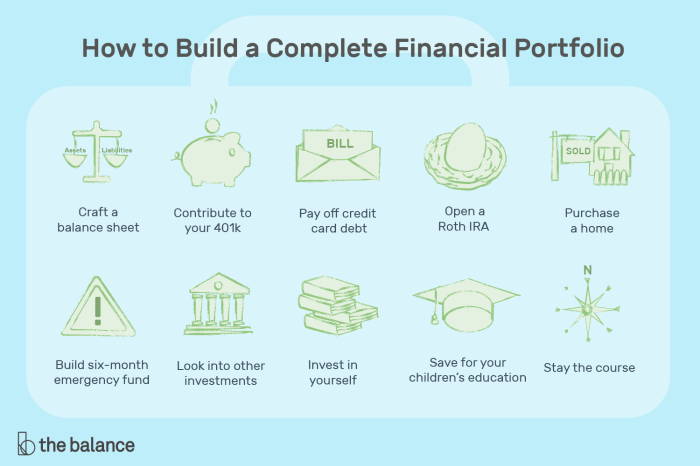
When it comes to building a strong financial portfolio, there are several key strategies that investors can follow to maximize their returns and minimize risk. By carefully selecting appropriate assets, setting clear financial goals, and regularly monitoring and rebalancing the portfolio, investors can create a well-diversified and resilient investment portfolio.
Steps for Creating a Financial Portfolio
Creating a financial portfolio from scratch involves several key steps:
- Evaluate your financial goals: Determine your short-term and long-term financial objectives, such as retirement planning, saving for a major purchase, or generating passive income.
- Assess your risk tolerance: Understand how much risk you are willing to take on in your investments and choose assets that align with your risk tolerance.
- Select appropriate assets: Choose a mix of assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities based on your financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Diversify your investments: Spread your investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions to reduce risk.
- Monitor and rebalance: Regularly review your portfolio performance, make adjustments as needed, and rebalance your investments to maintain your desired asset allocation.
Tips for Selecting Appropriate Assets
When selecting assets for your financial portfolio, consider the following tips:
- Align assets with financial goals: Choose assets that align with your investment objectives, whether it’s capital appreciation, income generation, or wealth preservation.
- Consider risk and return: Balance risk and return by diversifying your investments across different asset classes with varying levels of risk.
- Understand correlation: Select assets with low correlation to each other to further diversify your portfolio and reduce overall risk.
Role of Regular Monitoring and Rebalancing
Regular monitoring and rebalancing are essential to maintaining a strong financial portfolio:
- Monitor performance: Keep track of how your investments are performing relative to your financial goals and make adjustments accordingly.
- Rebalance portfolio: Adjust your asset allocation periodically to ensure that it stays in line with your risk tolerance and investment objectives.
- Stay informed: Stay up to date on market trends, economic developments, and changes in the investment landscape to make informed decisions about your portfolio.
Considerations for Risk Management in Financial Portfolio
Risk management plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and growth of a financial portfolio. It involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating the potential risks that could impact investments. By implementing effective risk management strategies, investors can protect their assets and optimize their returns.
Tools and Techniques for Managing Risks in Investments
Risk management in a financial portfolio can be achieved through various tools and techniques, including:
- Asset Allocation: Diversifying investments across different asset classes can help reduce overall risk exposure.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Setting predetermined price levels to automatically sell an asset can limit potential losses.
- Hedging: Using financial instruments like options or futures to offset potential losses in the portfolio.
- Risk Assessment: Regularly evaluating the risk profile of investments to make informed decisions.
Setting Realistic Expectations and Emergency Fund for Risk Mitigation
It is essential for investors to set realistic expectations regarding their investment goals and risk tolerance. By understanding the potential risks involved, investors can make well-informed decisions. Additionally, having an emergency fund separate from the investment portfolio can provide a financial cushion during unexpected market downturns or emergencies. This fund should ideally cover at least three to six months’ worth of living expenses to mitigate any financial setbacks.
